Difference between Mitosis and Meiosis
Last reviewed by Editorial Team on February 8th, 2019.
Cellular division is a must in order for cells to replicate. Separation of cells is done in two processes: mitosis and meiosis.
Although these two processes are similar, they both have differences, specifically in the processes involved and the resulting productions.
One of the primary differences between mitosis and meiosis is the class of cell they create. Mitosis reproduces somatic cells while meiosis reproduces germ cells. (1, 2, and 3)
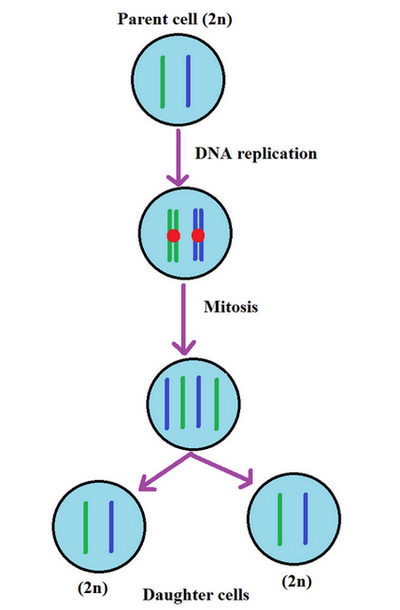
Picture 1: Two daughter cells were produced from a single mother cell.
Image source : cloudfront.net
The process of mitosis
The process of mitosis is the only form of cellular reproduction in single-celled organisms.
A single round of mitosis leads to two identical cells. In bacterial reproduction, mitosis leads to the production of new and independent organisms.
The reproduction process is asexual in nature because it does not require sex to create new organisms. In humans (multi-cellular organisms), mitosis only takes place in somatic cells.
During the process of mitosis, the chromosomes of the cells are duplicated leading to the formation of cells with two times more their usual haploid or diploid numbers.
Sister chromosomes are formed because the two resulting chromosomes are identical. Eventually, the two sister chromatids separate and a copy of each chromosome lines up on the cell’s opposite ends.
The cell’s center is pinched causing the cell to break into two distinct cells. Each cell has a chromosome and a nucleus will eventually form.
The end product is two cells with an identical number of chromosomes as the pre-existing cell. (3, 4, and 5)
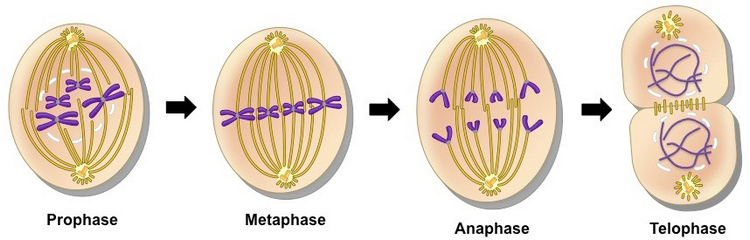
Picture 2 : The image above shows the different stages of mitosis.
Image source : bioninja.com
Stages/Phases
- Prophase
- Metaphase
- Anaphase
- Telophase (5)

Picture 3: Meiosis results in the formation of four daughter cells.
Image source:wikipedia.org
The process of meiosis
Unlike mitosis, meiosis is a complex process. It undergoes two cellular divisions. Meiosis produces germ cells, which are haploid in nature. Sexual reproduction needs to take place for the process of meiosis to take place.
There are two sex cells (gametes) and these are the sperm and egg cells. A sperm cell is the one produced by male whereas the egg cell is the one produced by the female. A sperm cell needs an egg cell for the reproduction to take place. It is the sperm cell that activates the egg cell through fertilization.
Two haploid cells unite resulting in a diploid cell. The resulting offspring will have the genetic characteristics of both parent genes. (5, 6, and 7)
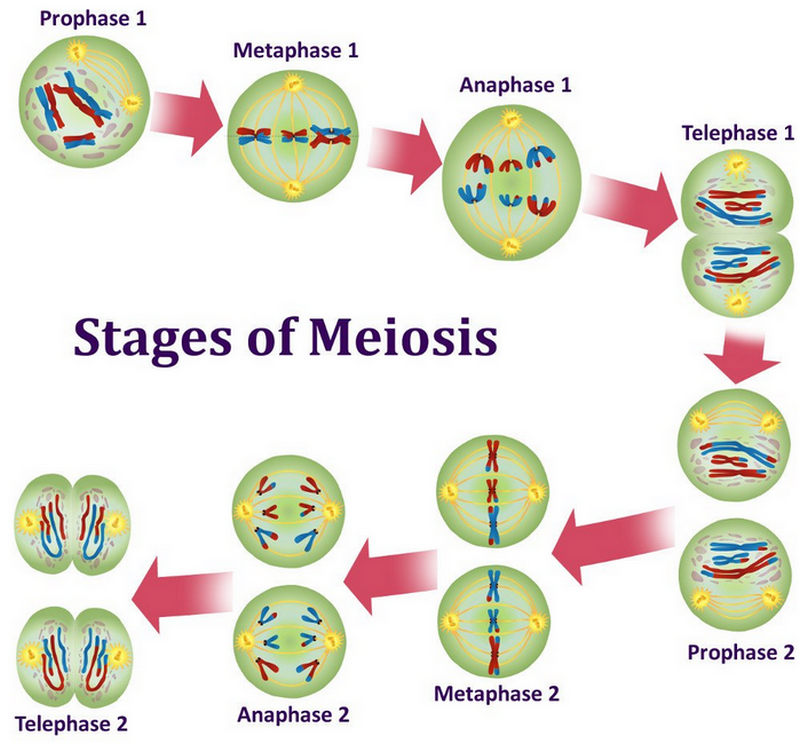
picture 4: the stages of meiosis.
Image Source: scienceabc.com
Stages/Phases
-
Meiosis I
- Prophase I
- Metaphase I
- Anaphase I
- Telophase I (6)
-
Meiosis II
- Prophase II
- Metaphase II
- Anaphase II
- Telophase II (6)
Are there any similarities?
- They both have interphase wherein the cell replicates the genetic composition and organelles to prepare for cellular division.
- They both have prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
- They both include lining up of sister chromatids along the metaphase plate.
- They both involve sister chromatids separation and formation of daughter chromosomes.
- They both end with cytoplasm division resulting in individual cells. (7, 8, and 9)
What are the difference between mitosis and meiosis?
Reproduction type
- Mitosis – Asexual reproduction
- Meiosis – Sexual reproduction
Number of division
- Mitosis – One
- Meiosis – Two
Homologs pairing
- Mitosis – No
- Meiosis – Yes
Where it takes place?
- Mitosis – Somatic cells
- Meiosis – Germ cells
Cell division
- Mitosis – The somatic cell undergoes division only once. The actual division process takes place at the end of telophase.
- Meiosis – The reproductive cell undergoes division twice. The division process takes place at the end of the first and second telophase.
Resulting daughter cells
- Mitosis – This process produces two daughter cells and each cell is diploid and contains the same number of chromosomes.
- Meiosis – This process leads to the formation of four daughter cells wherein each is haploid. It contains only a portion of chromosomes of the mother cell.
Genetic compositions
- Mitosis – The daughter cells are identical. Crossing over or recombination is not allowed.
- Meiosis – The end product contains various gene combinations secondary to the split of homologous chromosomes into various cells. The crossing over process is allowed, which is also one of the responsible for the different combination of genes.
Formation of tetrad
- Mitosis – No tetrad formation.
- Meiosis – A tetrad formation occurs (a close line up of pairs of homologous chromosomes)
Duration of prophase
- Mitosis – The length of prophase is shorter when compared to meiosis.
- Meiosis – The first prophase has five stages. This alone shows that meiosis’s prophase takes longer than mitosis.
Alignment of chromosomes in metaphase
- Mitosis – The sister chromatids are aligned at the metaphase plate.
- Meiosis – The pairs of homologous chromosomes are aligned at the metaphase plate in metaphase.
Separation of chromosomes
- Mitosis – The sister chromatids separate during anaphase and migrate centromere towards the cell’s opposite pole.
- Meiosis – The homologous chromosomes migrate towards the cells opposite poles during the first anaphase. (1, 5, 9, and 10)
Difference between mitosis and meiosis table
| Point of comparison | Mitosis | Meiosis |
| Reproduction type | Asexual reproduction | Sexual reproduction |
| Number of cellular division | One | Two |
| Homologs pairing | No | Yes |
| Where it takes place | Somatic cells | Germ cells |
| Resulting daughter cells | Two daughter cells (each is diploid and has the same number of chromosomes) | Four daughter cells and each cell is haploid. The number of chromosomes is the same as the original cell |
| Genetic compositions | Daughter cells are identical | The daughter cells have various gene combinations |
| Tetrad formation | No | Yes |
| Length of prophase | Shorter when compared to meiosis | Longer than mitosis |
| Alignment of chromosomes in metaphase | Sister chromatids are aligned at the metaphase plate | Homologous chromosomes are aligned at the metaphase plate |
| Separation of chromosomes | Sister chromatids separate during anaphase and migrate centromere towards the opposite pole of the cell | Homologous chromosomes migrate towards the cells opposite poles during the first anaphase (2, 5, and 8) |
References :
- https://www.sparknotes.com/biology/cellreproduction/intro/section2/
- https://www.thoughtco.com/differences-between-mitosis-and-meiosis-373390
- https://www.mytutor.co.uk/answers/17268/A-Level/Biology/What-is-the-differences-between-mitosis-and-meiosis/
- https://microbiologyinfo.com/differences-between-mitosis-and-meiosis/
- https://biologywise.com/difference-between-mitosis-meiosis
- https://www.biologyexams4u.com/2012/09/difference-between-mitosis-and-meiosis.html#.XCz7mjAzbZY
- https://www.bioexplorer.net/differences-between-mitosis-and-meiosis.html/
- https://www.yourgenome.org/facts/mitosis-versus-meiosis
- https://sciencetrends.com/key-similarities-differences-mitosis-meiosis/
- https://biodifferences.com/difference-between-mitosis-and-meiosis.html
Similar Posts:
- Difference between T Cells and B Cells
- Difference between Endotoxin and Exotoxin
- Buffy Coat
- Glycolysis Pathway – Definition and Summary
- Glycolysis Cycle – Steps and Enzymes (with Diagrams) In-Detail
